Spray Drying solutions for R & D and Production
Mumbai, Maharashtra
Monday to Saturday
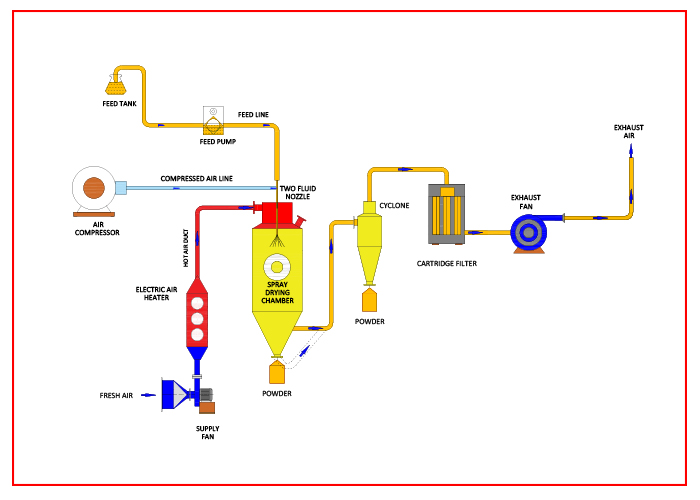
A laboratory spray dryer is a piece of equipment that is helpful in the pharmaceutical and food industries. For a laboratory spray dryer to operate effectively, it must have three important components: the atomiser, drying chamber, and heat exchanger by understanding the important components and how your laboratory spray dryer can produce high-quality results.
Atomiser
The atomiser is the spray dryer component responsible for generating material droplets. The atomiser is responsible for breaking up the solution into small droplets to distribute it evenly. Without an atomiser, the even distribution of the answer is impossible and could result in uneven drying.
Similarly, the heater provides the necessary heat to evaporate the solvent. Finally, the collector ensures the precise collection of the end product, so it does not end up on the floor or in the air. Atomisers come in various designs, such as nozzle and rotary atomisers. Nozzle atomisers use a high-pressure air stream to break the liquid into droplets. To atomise the liquid into droplets, rotary atomisers use a rotating disk or rotor to atomise liquid into droplets.
Laboratory spray dryers typically use nozzle atomisers because they can produce smaller droplets than rotary atomisers.
The size of the droplets determines how quickly the drops will evaporate and also affects the surface area of the final powder product. Smaller drops will evaporate more rapidly and produce a powder with a larger surface area.
The atomiser is an essential part of the spray dryer because it affects the quality of the final product. If the atomiser is not working properly, it can result in an uneven or poor-quality powder. Regular cleaning and maintenance will ensure that the atomiser works properly and produces a high-quality powder.
Drying Chamber
The drying chamber is where the actual drying process takes place. It typically has a fan that circulates hot air through the chamber. The atomiser feeds the material that needs to dry into the chamber, where it comes into contact with the hot air and starts to evaporate.
The drying chamber is the heart of the laboratory spray dryer. It is where the liquid material transforms into a powder or granulate form. The size and shape of the drying chamber will vary depending on the type of spray dryer. Some have a cylindrical chamber while others have a square or rectangular one. The chamber will also have a heating element to help speed up the drying process. Different types of nozzles are beneficial in the drying chamber. These include flat fan, spiral, and disk nozzles. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages.
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger is responsible for heating the air that circulates through the drying chamber. There are various heat exchangers, but the plate heat exchanger is the most common. The plate heat exchanger consists of a series of metal plates separated by a thin fluid layer. As the hot air from the drying chamber passes through the heat exchanger, it transfers its heat to the fluid, which in turn heats the air on the other side of the exchanger.
A heat exchanger is a vital component in a laboratory spray dryer. There are two types of heat exchangers: Air-cooled and water-cooled. Air-cooled heat exchangers are less expensive and easier to maintain but are not as efficient as water-cooled. Water-cooled heat exchangers are more expensive, but they are more efficient.
Factors to consider:
The unit's efficiency is the most important factor to consider when selecting a heat exchanger. The unit's efficiency will determine the required energy to operate the spray dryer. A higher efficiency unit will require less energy and will result in lower operating costs. Another factor to consider is the size of the heat exchanger. The size of the heat exchanger determines the amount of heat that can be transferred to the sample. A larger heat exchanger can provide more heat, but it will also be more expensive.
The type of spray dryer you select will also impact the type of heat exchanger you need if you use a laboratory spray dryer for small batches. However, if you are using a production spray dryer, then a water-cooled heat exchanger will be required.

Head of Innovation
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Benenatis mauris. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in industry, logistics, finance, business orci ultrices venenatis mauris.
Marketing
92%
Marketing
82%